5G is the fifth generation of wireless network technology. The main theme of 5G is speed. Every new generation of wireless networks is significantly faster and more capable than the previous.
Some of you may remember the old and very slow – 2G and 3G. And currently, we are all using 4G – the mobile network that is used around the world to make calls, send messages and surf the web. And we can see how much better 4G is than 2G and 3G.
5G represents another step forward. It is said to be this new, faster network that has the potential to transform the Internet. And currently, network service providers all over the world are working on building their 5G networks.
How 5G works?
So take advantage of 5G, you need a 5G device – for example Samsung Galaxy S10 – with 5G radio frequency and a 5G network.
5G is built on millimetre waves. It’s a new section of a very high-frequency spectrum, upwards of 20 GHz all the way to near 96 GHz. But the catch is – the higher the frequency of any wave, the lesser the range.
It is the same reason why 5GHz Wi-Fi does not travel as far as 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi. Also, the same reason why microwaves do not cook things on the other side of the microwave door. So in an essence, 5G does not travel well in the real world.
Even if you’re standing up pretty close to the 5G node, it only travels well within direct line-of-sight. So things like trees, walls and buildings can block and disrupt the high-frequency signal. Even if you are still close to it.
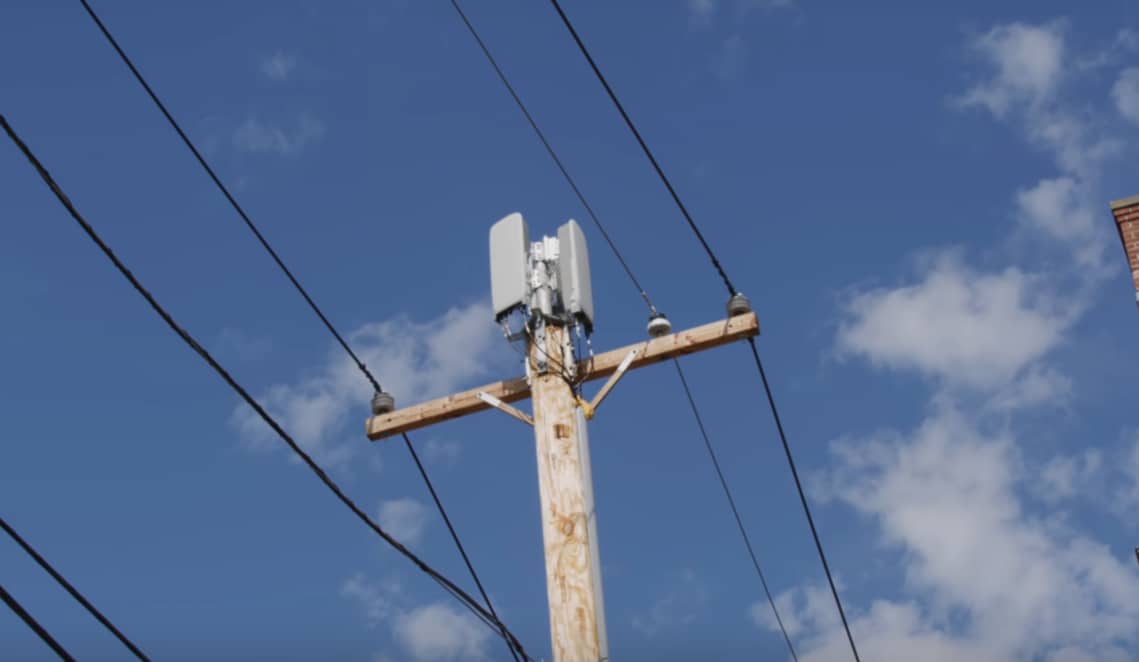

There are even claims saying that rain in the air could potentially disrupt 5G’s range.
How fast is 5G?
But if you’re standing right next to a 5G node with a compatible phone in your hand and run a speed test, the result is absolutely amazing. We are talking about over 1,000 Mbps (1 Gbps) for download speed. It is so fast you could finish up your monthly mobile data limit in minutes!
High-definition (HD) YouTube videos would just play instantly without any buffering. You could fast forward right off the bat, no problem. Web browsing would be super fast. Hopping into the Play Store to download a gigantic game like PUBG Mobile (2.05 GB) – it progresses pretty fast, but not like a blink of an eye.
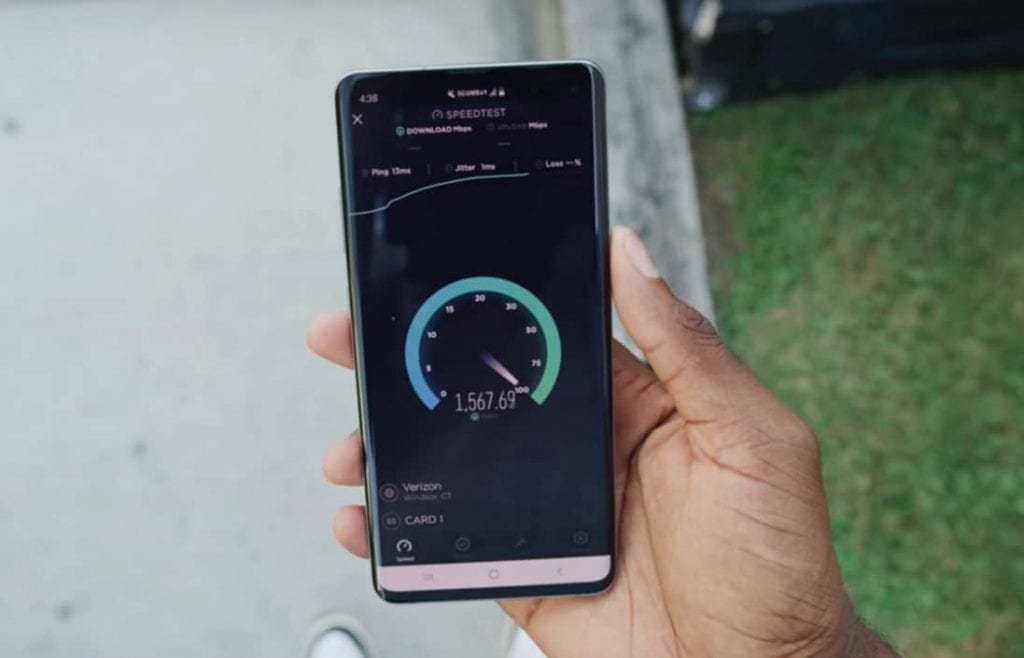
The Fortnite downloader progresses faster than the Fortnite installer. Downloading an episode of Stranger Things on Netflix in HD takes about four seconds. So you could download the whole season in probably like 30 seconds.
Poor range
But here’s the thing. These are all done while standing right next to the tower (where the 5G nodes are located) with a direct line-of-sight and in perfect weather. But once you left that, the signal’s quality deteriorates pretty quickly.
For example, if there is a building or wall between you and the tower, you will be getting much slower speed which is about 200-400 Mbps. It is still 5G speed. And it is still kind of crazy to call 200-400 Mbps as ‘slow’, but compared to what you were getting before, that’s a pretty big difference.
Basically your download speed halves (even lower) by just walking a couple of meters away from the tower. As you’re walking further away, your phone would start bouncing back and forth between 4G and 5G – indicating 5G’s poor range.
To combat this weakness, network service providers would put a lot of nodes all over the place to maximize coverage within a city. So when you move behind one obstacle to another (as you would do when driving around a city), you would actively switch between nodes that you are connected to – like what we do now with 4G towers. Only much faster.
But to build these 5G towers all over a city – much less a country, it requires significant cost and a very long time. Extensive building and running costs will force operators to share the use and management of the mobile network.
Energy-gulping connection
There are a few drawbacks to note in 5G as well.
Firstly, the 5G’s upload speed is still pretty much the same as 4G. The ping level is still at 4G level. So our dream to see an 8k YouTube video in a matter of seconds is still a pipedream – at least at the time of this writing.
The heat a 5G connection causes to 2019 smartphones is something to take note as well. You could feel the warmth on the back of Samsung Galaxy S10 upon four to five hours of just web browsing and video watching. And as a result, the battery life suffers too.
This maybe explains why you see almost every 5G smartphones are equipped with larger batteries than its 4G predecessors.
So in conclusion, 5G is kind of like foldable phones in 2019. It is clearly not ready yet, but it has enormous potential. When you use it in the right place and setting, you would get a glimpse of the future – which is amazing.
Right now, the cons outweigh the pros. But with the inevitable advancement of infrastructures, 5G would give us a world filled with unthinkable possibilities.
It may not happen overnight, but 5G is coming.
